Introduction
As a Javascript Developer, we used the console.log() method a lot of times to display the result of your code. Now, think that you are writing some Js code and it doesn't work correctly. What's the first thing you do? You are console.logging it! . This article gives you a basic understanding of console methods.
What is Console ?
The console is the tool where you can test or check your code is working properly or not. It can be used to access the browser to troubleshoot the errors related to your code. Remember a console is an object that can access the methods like log() using the dot (.) operator.
Syntax:
Object.Method(parameters);
1. Using Destructing Javascript
Destructuring Assignment is a JavaScript expression that allows to unpack values from arrays, or properties from objects, into distinct variables data can be extracted from arrays, objects, nested objects and assigning to variables. In Destructuring Assignment on the left-hand side defined that which value should be unpacked from the sourced variable.
Usage: By using the destruction power of javascript objects, you can do this:
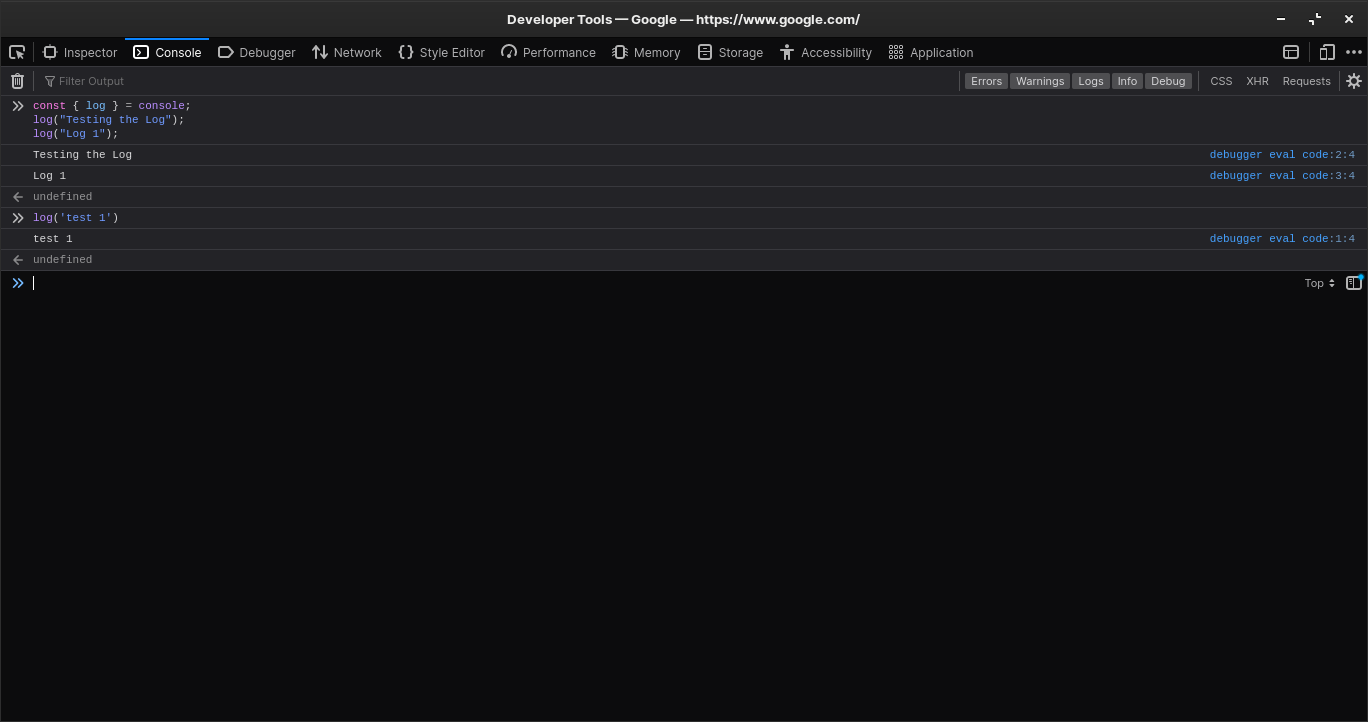
const { log } = console;
log("Testing the Log");
log("Log 1");
You can change the log function to any other name you want like this:
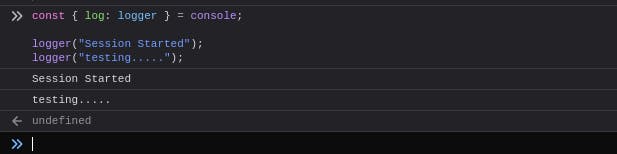
const { log: logger } = console;
logger("Session Started");
logger("testing.....");
2. Console Info
The console.info() is a method in JavaScript that is used to display the important messages to the console. Usage:
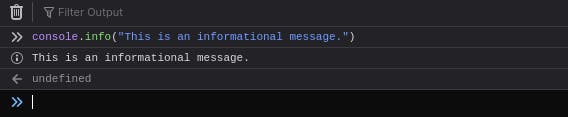
console.info("This is an informational message")
In firefox you can see an i icon near to the message indicating it's informational
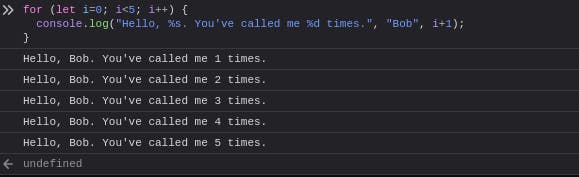
We can also use string substitution and additional arguments with this method.
for (let i=0; i<5; i++) {
console.log("Hello, %s. You've called me %d times.", "Bob", i+1);
}
3. Console Group
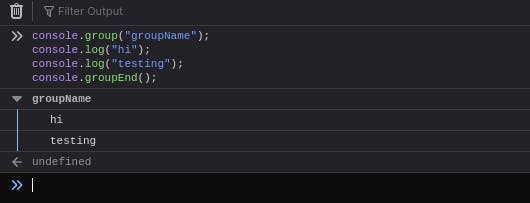
Ever wanted to group your logs? This method is perfect for you!
console.group("groupName");
console.log("hi");
console.log("testing");
console.groupEnd();
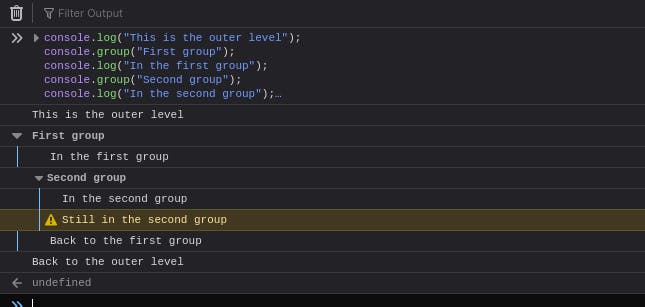
You can also have sub groups,
console.log("This is the outer level");
console.group("First group");
console.log("In the first group");
console.group("Second group");
console.log("In the second group");
console.warn("Still in the second group");
console.groupEnd();
console.log("Back to the first group");
console.groupEnd();
console.debug("Back to the outer level");
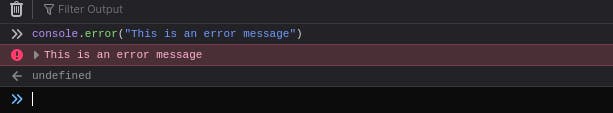
4. Console Error
This method is used to find out errors in the code. Console.error() method is developed for debugging.
Syntax :
console.error(parameter);
5. Console Table
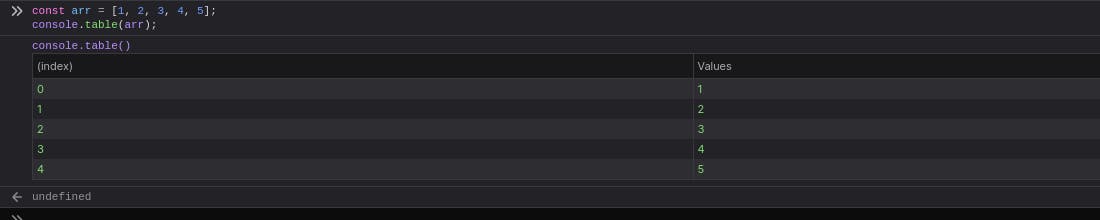
The console.table() method displays tabular data as a table.
This function takes one mandatory argument data, which must be an array or an object, and one additional optional parameter columns.
It logs data as a table. Each element in the array (or enumerable property if data is an object) will be a row in the table.
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.table(arr);
6. Console Time
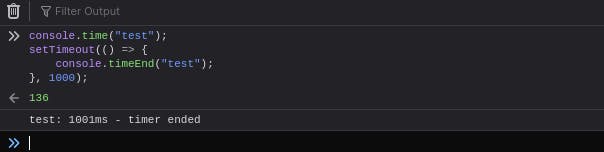
The console.time() method starts a timer you can use to track how long an operation takes. You give each timer a unique name, and may have up to 10,000 timers running on a given page. When you call console.timeEnd() with the same name, the browser will output the time, in milliseconds, that elapsed since the timer was started.
console.time("test");
setTimeout(() => {
console.timeEnd("test");
}, 1000);
7. Console Assert
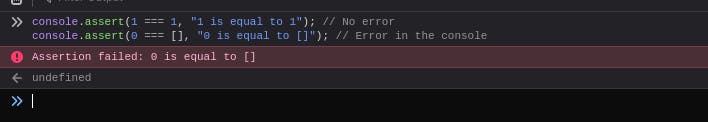
The console.assert() method writes an error message to the console if the assertion is false. If the assertion is true, nothing happens.
console.assert(1 === 1, "1 is equal to 1"); // No error
console.assert(0 === [], "0 is equal to []"); // Error in the console
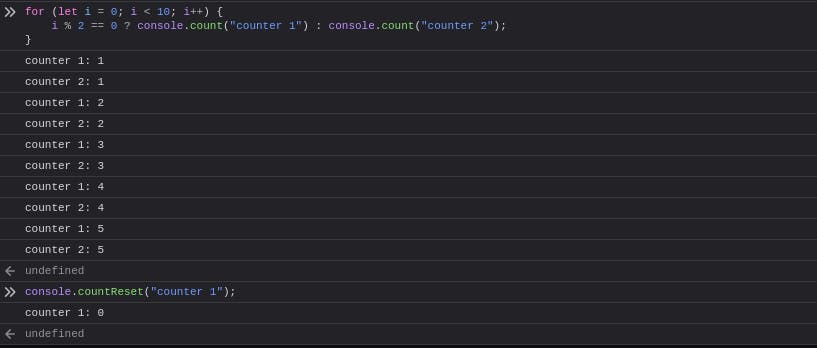
8. Console Count
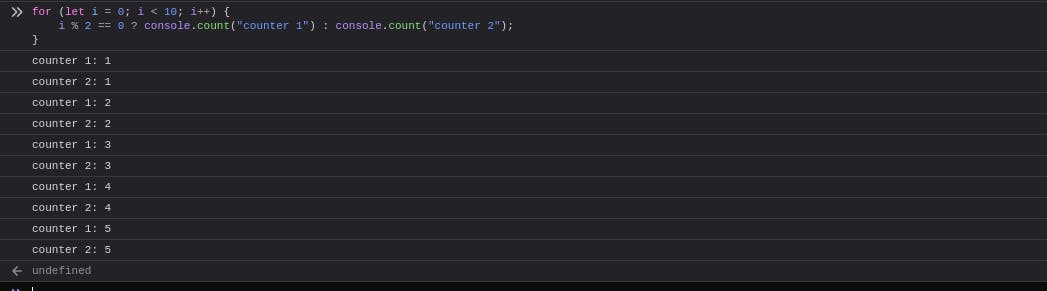
Count the number of times a certain thing happens.
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
i % 2 == 0 ? console.count("counter 1") : console.count("counter 2");
}
9. Console CountReset
Resets the value of the counter with the given label.
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
i % 2 == 0 ? console.count("counter 1") : console.count("counter 2");
}
console.countReset("counter 1");
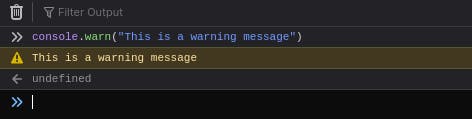
10. Console Warning
If something goes wrong then this method is used to display warning messages to the console.
Syntax :
console.warn(parameter);
console.warn("This is a Warning");
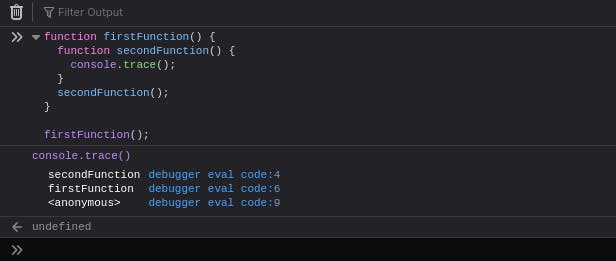
11. Console Trace
The console.trace() method tracks the execution of the code from starting point to the endpoint and how the code ended at a certain point.
Syntax :
console.trace(label);
This method accepts any data as a single parameter.
function firstFunction() {
function secondFunction() {
console.trace();
}
secondFunction();
}
firstFunction();
References:
- MDN Web docs - developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/co..
- dev.to blog - dev.to/fatematzuhora/different-use-cases-of..